What is the FIB-4 Index?
The FIB-4 Index Calculator is a simple, non-invasive score calculator that helps you understand if your liver might be affected by fibrosis (liver scarring). The FIB-4 index was originally developed to assess advanced fibrosis in patients co-infected with HIV and Hepatitis C. It uses three routine blood test values, Age, AST, ALT, and Platelet Count, to give you a reliable idea of your liver health without needing a biopsy.
✅ Non-invasive: No biopsy needed
✅ Cost-effective: Based on regular tests
✅ Early detection: Helps detect silent fibrosis
✅ Screening-ready: Ideal for community and primary care levels
✅ Monitors trend: Repeatable over time to track progress or deterioration
Whether you’re managing fatty liver / NAFLD/ MASLD, MASH, or concerned about long-term cardiovascular risks, this index will give you clarity.
Why is determining the severity of liver disease important?
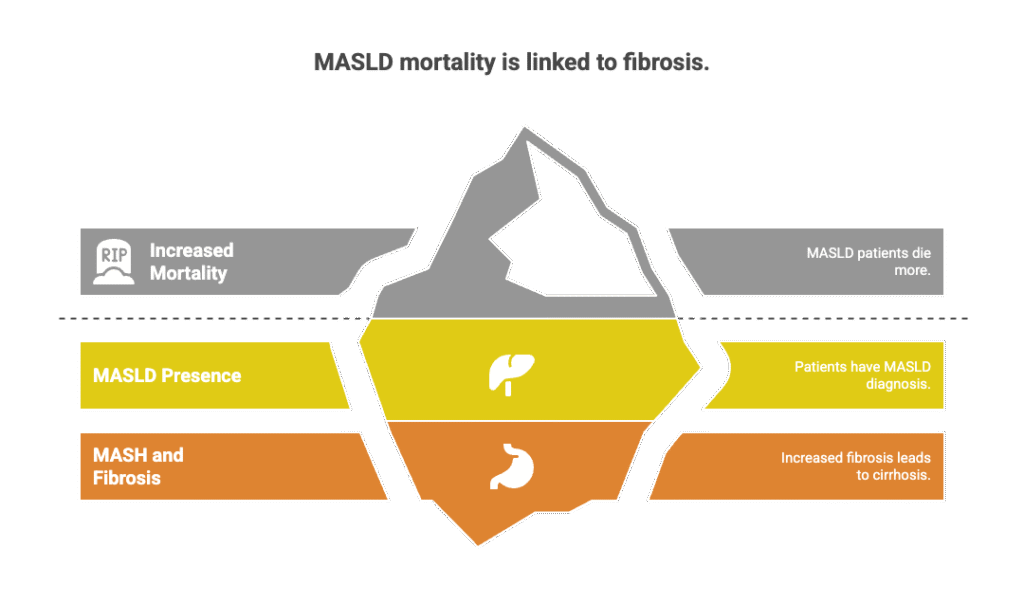
The overall mortality rate for people with MASLD is higher than that of those without MASLD (metabolic associated liver disease / fatty liver disease).
Patients with MASH and increasing fibrosis are more likely to develop cirrhosis and die from liver disease, according to mounting data.
How is the FIB-4 Index Calculated?
🧮 The formula:
FIB-4 Index = (Age × AST) ÷ (Platelet Count × √ALT)
- Age in years
- AST & ALT are liver enzymes (in U/L)
- Platelet Count in 10⁹/L
No need to remember this, just enter your values in our calculator below!
🚀 Ready to Use the FIB-4 Index Calculator? Check your score below 👇⏬
📊 FIB-4 Index Calculator
Enter the values below to calculate the FIB-4 index for liver fibrosis.
❓ How Do We Interpret the FIB-4 Index?
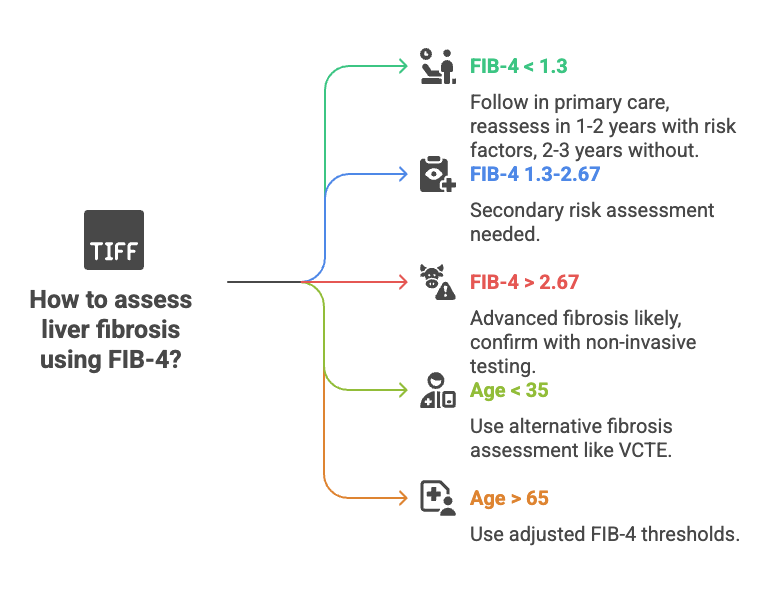
- < 1.3 (or 1.45 in some studies): Low risk of advanced fibrosis. High negative predictive value (NPV).
- 1.3–3.25: Intermediate risk. Further testing, like FibroScan or elastography recommended.
- > 3.25: High risk of advanced fibrosis. Consider referral to a hepatologist.
A higher FIB-4 cut-off of 2.0 for older patients.
🔍 High NPV means FIB-4 is excellent to rule out fibrosis when the score is low.
The FIB-4 index is a screening tool, not a diagnostic tool. For a definitive diagnosis, patients must be thoroughly assessed by a clinician. This tool helps identify individuals at risk, allowing them to screen whether they need further evaluation. While the FIB-4 score provides a snapshot, the trend of follow-up scores is far more significant than any single score, offering better insight into the patient’s overall prognosis.
The American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) recommends the use of the FIB-4 index score as an initial assessment tool for patients with fatty liver, particularly to exclude advanced fibrosis and monitor those at ongoing risk of MASH and cirrhosis; further evaluation by a hepatologist may be necessary to determine if additional assessments, such as FibroScan, elastography, MRI, or liver biopsy, are required.
Explore more free tools, liver-friendly guides, and evidence-based articles on our website livertransplanthelp.com.
Why the FIB-4 Index Matters
The FIB-4 Index Score is more than a number. Trends are more important has prognostic significance.
According to a 2024 study by Anstee et al. in The Lancet Regional Health – Europe, a high FIB-4 Index score is linked with:
📌 Increased risk of liver-related events
📌 Higher risk of cardiovascular events
📌 All-cause mortality, especially in people with obesity, metabolic syndrome, and Type 2 diabetes
✅ Low FIB-4 Score = Low risk of advanced fibrosis
⚠️ High FIB-4 Score = May need specialist referral or FibroScan
It’s now used worldwide for routine liver risk screening in clinics, especially in people without symptoms.
Use Cases of the FIB-4 Index
You can use the FIB-4 Index if you have:
- NAFLD (Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease)
- MASH (Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis)
- Alcoholic liver disease
- Hepatitis B and C
- HIV with co-infection
- Autoimmune Hepatitis
- Type 2 Diabetes
- PCOS with insulin resistance
- Obesity or central abdominal fat
🏥 The FIB-4 index Calculator is utilised by healthcare practitioners. To efficiently screen and prioritise patients, particularly in primary healthcare centres for community-based screenings.
Secondary Liver Risk Assessment Funnel (After High FIB-4 Score)
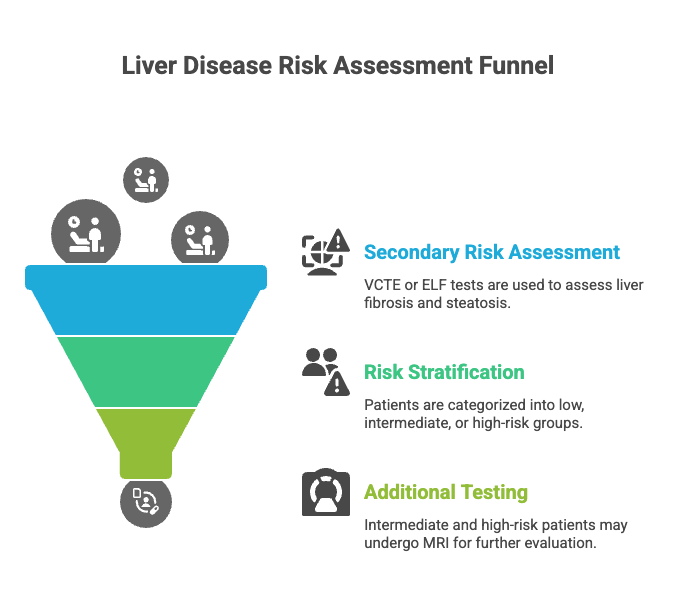
🔹 Step 1: Confirmatory Assessment Needed
- If the FIB-4 score is high, it indicates potential advanced fibrosis.
- Proceed to secondary risk assessment using:
- Transient elastography (FibroScan/VCTE)
- OR ELF test (Enhanced Liver Fibrosis)
📍 Secondary Risk Assessment Tools
✅ Transient Elastography (FibroScan/VCTE)
- Evaluates both fibrosis and steatosis.
- CAP score (Controlled Attenuation Parameter) reflects fat content in the liver:
- 100–400 dB/m range
- >238 dB/m = significant steatosis
- 238–260 dB/m: Grade 1 (≈33% liver affected)
- 260–290 dB/m: Grade 2 (≈34–66% liver affected)
- >290 dB/m: Grade 3 (≈67% or more affected)
- Fibrosis score (kPa):
- <8 kPa = Low risk
- >12 kPa = High risk
✅ ELF Test (Enhanced Liver Fibrosis)
- Blood test measuring fibrosis markers.
- Validated to detect advanced fibrosis in fatty liver disease.
- ELF score thresholds:
- <7.7 = Low risk
- >9.8 = High risk
🔬 Next Step Based on Stratification
- Risk categories based on FIbroscan/ ELF score :
- Low
- Intermediate
- High
- For high-risk patients:
- Consider additional tests, e.g., MRI for further evaluation.
How Accurate is the FIB-4 Index?
💡 It’s not perfect, but it’s very useful in low-resource settings or early-stage assessment. Someone with a Metabolic risk factor like Diabetes/ hypertension/dyslipidemia/obesity but a normal FIB-4 (<1.3) score still needs a repeat blood test and FIB-4 scoring 1-2 yearly, and as and when required doctor's consultation.
Clinical accuracy:
| Range | Interpretation | Recommendation |
| <1.3 | Low risk of fibrosis | Repeat after 2-3 years |
| 1.3–2.67 | Indeterminate zone | Refer to a liver specialist |
| >2.67 | High risk | Refer to liver specialist |
Performance Metrics (varies slightly by population):
- Sensitivity: ~60–70%
- Specificity: ~75–85%
- NPV (Negative Predictive Value): >90% in low-risk populations. A high NPV means that a low FIB-4 score indicates the probability that a patient does not have significant or advanced liver fibrosis.
- PPV (Positive Predictive Value): Increases in diabetics/obese patients
Limitations of the FIB-4 Index
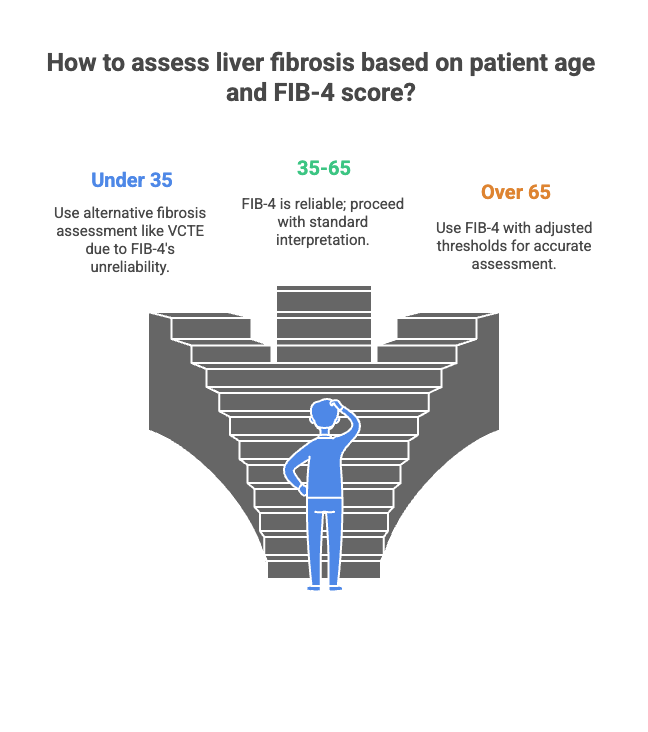
⚠️ Like all screening tools, it has limitations:
- Not very reliable in younger adults and old people(<35 years >65 years)
- ≤35 years: Use an additional fibrosis test (e.g., VCTE) along with FIB-4.
- ≥65 years: Apply age-adjusted FIB-4 thresholds:
- <2.0 → Advanced fibrosis unlikely
- 2.0–2.67 → Needs further NIT (e.g., VCTE)
- >2.67 → Advanced fibrosis likely
- Can be falsely high in acute infections or inflammation
- Doesn’t replace FibroScan or liver biopsy when indicated
- Platelet count may be affected by medications, infections, or other conditions
Use it as part of an overall evaluation, not in isolation.
Product Specification:
- Name: FIB-4 Index Calculator
- Category: Digital Health Screening Tool
- Description:
- The FIB-4 Index Calculator is a simple, user-friendly digital tool designed to assess the risk of liver fibrosis in patients using just four common blood parameters: Age, AST, ALT, and Platelet count. It helps in screening for liver conditions, particularly useful for individuals with fatty liver disease (NAFLD/NASH), hepatitis, or metabolic disorders.
How It Works:- Enter the patient's age, AST, ALT, and Platelet count into the designated fields.
- Click Calculate FIB-4 to get the score.
- The score result is displayed instantly, along with a brief interpretation of the risk level.
Key Features: - Easy to use and access.
- Non-invasive tool.
- Free of cost for immediate use.
- Instant results with interpretation of the score.
- Simple and efficient for primary care and home use.
- Suitable for monitoring the risk of NAFLD, MASH, Cirrhosis, and Fibrosis.
Star Rating:
- ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (5/5)
The FIB-4 Index Calculator is highly rated for its simplicity, accuracy, and reliability, making it a must-have digital tool for liver health assessment.
Disclaimer:
This calculator is for informational purposes only. Always consult your healthcare provider for medical advice.
Related Resources:
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the FIB-4 Index?
To assess the risk of liver fibrosis (scarring) using non-invasive lab markers.
What is the formula for calculating the FIB-4 Index?
(Age × AST) ÷ (Platelet Count × √ALT)
What is a good FIB-4 score?
Under 1.3 is typically considered low risk.
How do I interpret the FIB-4 result?
- <1.3 = Low risk
- 1.3–2.67 = Borderline
- 2.67 = High risk
Is the FIB-4 Index accurate?
Yes, especially for ruling out advanced fibrosis in people with metabolic risks. It has high NPV.
Is there a chart for the FIB-4 Index?
Yes! You’ll find it above with clear-cut-off zones and interpretations.
Can it be used in pregnancy or by children?
Not routinely recommended — other assessments are preferred.
Where Can I Use This Calculator?
You can use the FIB-4 Index calculator:
🖥️ On this page
📲 Embedded in any blog about fatty liver, post-transplant, hepatitis
📂 As part of your free digital product toolkit
🧾 With tracking tools in your Post-Transplant Recovery Kit
📲 Use It As A Digital Health Tool
You can now use the FIB-4 Index Calculator right here on our website. This is one of our free digital tools developed to help:
- Educate patients and caregivers
- Empower early screening at home or clinics
- Monitor disease progression non-invasively
- Integrate into primary care or public health programs
